Radiation Oncology
Radiation therapy is one of the three main pillars of cancer treatment, alongside surgery and chemotherapy. Globally, nearly 60% -70% of all cancer patients require radiation at some point during their treatment journey—either as a part of curative therapy, to shrink tumors before surgery (preoperative or neoadjuvant radiotherapy), or to relieve symptoms in advanced disease (palliative radiotherapy). It is a non-invasive, highly effective treatment modality that uses precisely targeted high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells while sparing surrounding healthy tissue.
At Andromeda Cancer Hospital, we recognize the critical role of radiotherapy in achieving long-term cancer control and cure. Whether used alone or in combination with other treatments, radiation contributes significantly to improving survival outcomes in cancers of the breast, head and neck, prostate, cervix, lung, brain, and more. With advances in imaging, planning, and delivery, today’s radiotherapy is more accurate, more effective and safer than ever before.
Equipped with the Varian TrueBeam STx, one of the most advanced linear accelerators available worldwide, our radiation oncology department offers cutting-edge treatment tailored to each patient’s specific needs. From conventional therapy to highly specialized techniques like image guided radiotherapy and stereotactic radiation, we bring the latest global standards of care to the people of Haryana and surrounding states of northern India.
Clinical Settings for Radiotherapy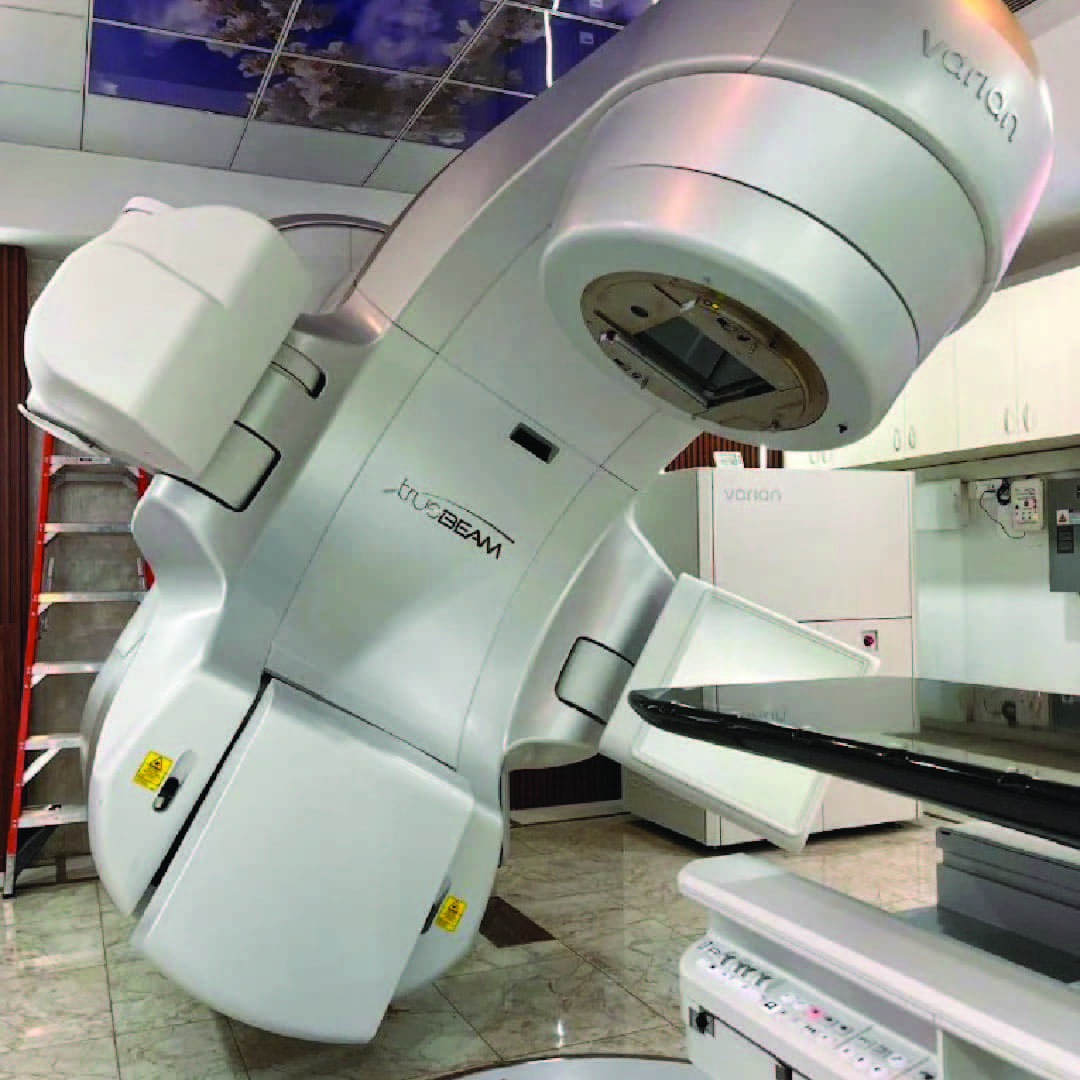
Radiation therapy is a versatile treatment that can be used in different stages of cancer care, depending on the disease type, stage, and treatment goals. At Andromeda Cancer Hospital, we use advanced radiotherapy techniques in the following clinical settings:
1. Radical (Definitive) Radiotherapy
This is used as the primary curative treatment, either alone or in combination with chemotherapy, particularly in cancers of the head and neck, cervix, prostate, and lungs. High-dose radiation is delivered with curative intent, especially when surgery is not feasible.
2. Neoadjuvant (Preoperative) Radiotherapy
Radiation may be given before surgery to shrink tumors and make them more operable. It is commonly used in rectal, esophageal, and certain sarcomas, and can improve surgical outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence.
3. Adjuvant (Postoperative) Radiotherapy
Following surgery, radiation is used to eliminate residual microscopic disease, lowering the risk of local recurrence. This is standard in breast cancer, brain tumors, head & neck cancers, and gynecological cancers.
4. Palliative Radiotherapy
When cure is not possible, radiation can be used to relieve symptoms such as pain, bleeding, or obstruction caused by advanced cancer. It significantly improves quality of life in patients with bone metastases, spinal cord compression, brain metastases, or bleeding tumors.
5. Prophylactic Radiotherapy
In select high-risk cases, radiation is used to prevent cancer spread to specific sites—e.g., prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) in small cell lung cancer to prevent brain metastases.

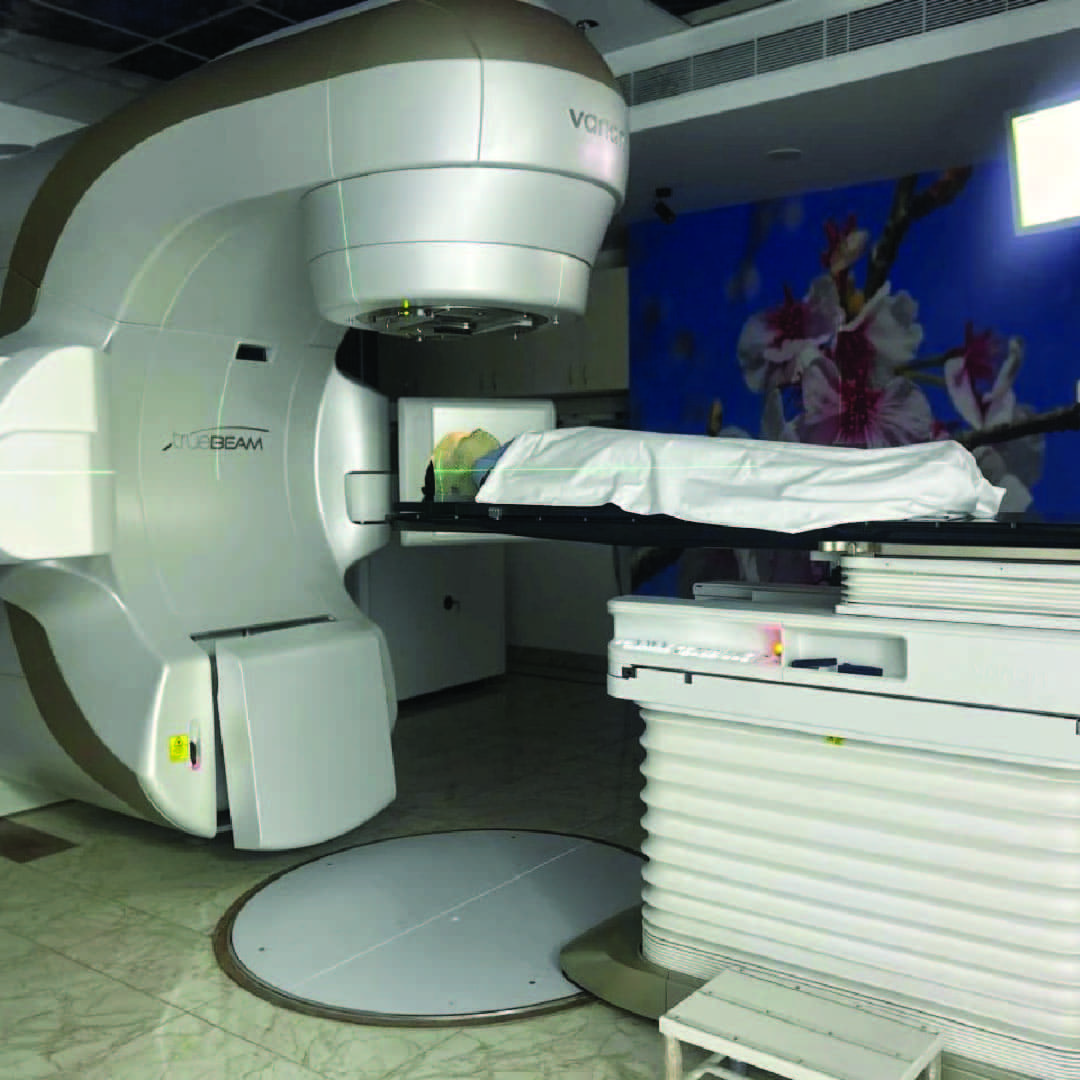
Our Technology: Varian TrueBeam STx
At Andromeda Cancer Hospital, we are proud to offer world-class radiotherapy with the Varian TrueBeam STx—a state-of-the-art linear accelerator designed for precision, speed, and versatility in cancer treatment. This advanced system delivers highly conformal radiation using technologies like IMRT, IGRT, volumetric arc therapy, SRT, SRS, and SBRT, allowing us to target tumors with sub-millimeter accuracy.
TrueBeam STx is equipped with a high-definition multi-leaf collimator (HD120 MLC) that shapes the radiation beam to match the exact dimensions of the tumor, reducing exposure to surrounding healthy tissue. It features high-dose rate (HDR) delivery and can complete complex treatments in just a few minutes, enhancing patient comfort and reducing motion-related uncertainties.
With real-time image guidance (including cone-beam CT) and respiratory gating systems, the machine tracks tumor position dynamically—even during breathing—making it ideal for treating tumors in moving organs like the lungs, liver, and breast. Its versatility allows us to treat a wide range of cancers including brain, spine, lung, liver, breast, prostate, and head & neck tumors, with extreme precision and reduced side effects.
Whether the goal is cure, control, or palliation, the TrueBeam STx enables us to deliver personalized radiation therapy with confidence, safety, and the latest global standards.
Rediation Oncology Techniques Offered
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)
IGRT uses real-time imaging (like cone-beam CT) before and during treatment to ensure exact tumor targeting. It improves accuracy and allows for tighter treatment margins, reducing side effects.
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
IMRT allows modulation of radiation intensity within each beam, enabling highly conformal dose distribution. This is particularly useful for treating tumors near critical organs such as in head & neck, prostate, and pelvic cancers.
Rapidarc (Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy or VMAT)
VMAT delivers radiation in a continuous arc around the patient, adjusting the intensity and shape dynamically. This technique shortens treatment time while maintaining high precision, ideal for complex and large tumors.
3D Conformal Radiation Therapy (3D-CRT)
3D-CRT uses CT-based imaging to shape radiation beams precisely to the tumor’s size and shape. It helps limit exposure to nearby normal tissues while effectively treating the cancer.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy (SRS/SRT)
SRS/SRT delivers a single or few high-dose radiation sessions with sub-millimeter precision, typically for brain and spine tumors. It offers a non-surgical option for inoperable or deep-seated lesions.
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT)
SBRT is used for treating small, well-defined tumors in organs such as lung, liver, adrenal, and prostate with very high doses over 1–5 sessions. It provides excellent local control with minimal impact on surrounding healthy tissues.
Respiratory Gating
(e.g. Deep Inspiratory Breath Hold (DIBH) for Left-Sided Breast Cancer)
DIBH is a specialized technique used to reduce radiation dose to the heart by treating while the patient takes a deep breath. It is particularly beneficial in left-sided breast cancer to minimize cardiac risks.
Total Body Irradiation (TBI)
TBI is used as part of conditioning before bone marrow or stem cell transplantation, delivering uniform radiation across the entire body to eliminate residual cancer cells.
Total Marrow Irradiation (TMI)
TMI is a more targeted form of TBI that selectively irradiates the bone marrow while sparing healthy organs, offering a safer preparative regimen for hematological cancers.
Total Skin Electron Irradiation (TSEI)
TSEI is used to treat cutaneous lymphomas and other widespread skin malignancies by delivering low-penetration electron beams uniformly over the entire skin surface.
Cancers Treated with Rediation Oncology
At Andromeda Cancer Hospital, we use advanced radiation techniques to treat a wide range of cancers. Radiotherapy may be used alone or in combination with surgery and chemotherapy, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
1. Head and Neck Cancers
Radiation is a cornerstone treatment for cancers of the oral cavity, oropharynx, larynx, hypopharynx and nasopharynx. It is used either as definitive or as adjuvant therapy to preserve organ function and/or achieve long-term control.
2. Breast Cancer
Postoperative (adjuvant) radiation is standard after breast-conserving surgery and is required many times after mastectomy to reduce the risk of local and/or regional recurrence. We also offer Deep Inspiratory Breath Hold (DIBH) for left-sided breast cancers to minimize radiation dose to the heart. Accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) is also used as applicable.
3. Prostate and Genitourinary Cancers
Radiation is a curative option for localized prostate cancer and can also be used after surgery for recurrence. Advanced techniques like IGRT and VMAT allow precise delivery near sensitive organs such as the bladder and rectum.
4. Gynecological Cancers
Radiation is a very important component of management of gynecological cancers. Cancer of uterine cervix is often treated with curative radiotherapy. Adjuvant radiation is a common component of endometrial cancer treatment. Cancers of vulva and vagina also often need radiation as part of treatment.
5. Lung and Esophageal Cancer
Radiotherapy is used in definitive, neoadjuvant, or palliative settings for thoracic cancers. SBRT is especially effective for early-stage, inoperable lung tumors, offering high control rates with minimal sessions.
Neoadjuvant radiotherapy or chemo-radiotherapy is commonly used for esophageal cancers, especially squamous cell carcinoma.
6. Gastrointestinal Malignancies
Radiation is commonly used in rectal, anal, pancreatic, and esophageal cancers—either before surgery to shrink tumors or after to eliminate microscopic disease. It may also be used for palliation in advanced disease.
7. Brain and Spine Tumors
We use highly focused techniques like SRS (Stereotactic Radiosurgery) and IMRT to treat both primary brain tumors and metastases with precision. Radiotherapy helps control growth, reduce symptoms, and protect surrounding neurological structures.
8. Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors
Radiation is used in soft tissue sarcomas for limb preservation and in bone metastases for effective pain relief. Stereotactic techniques are useful for treating spinal tumors and preventing cord compression.
9. Pediatric Cancers
In children, radiation is used cautiously and precisely, especially in brain tumors, Wilms tumor, and sarcomas. Our pediatric protocols aim to balance effective treatment with long-term safety and developmental preservation.
10. Hematological Cancers
Radiation is a useful component of treatment of hematological malignancies. It is used in Hodgkin’s disease as well as non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood component irradiation can also be used in patients with hematological malignancies.
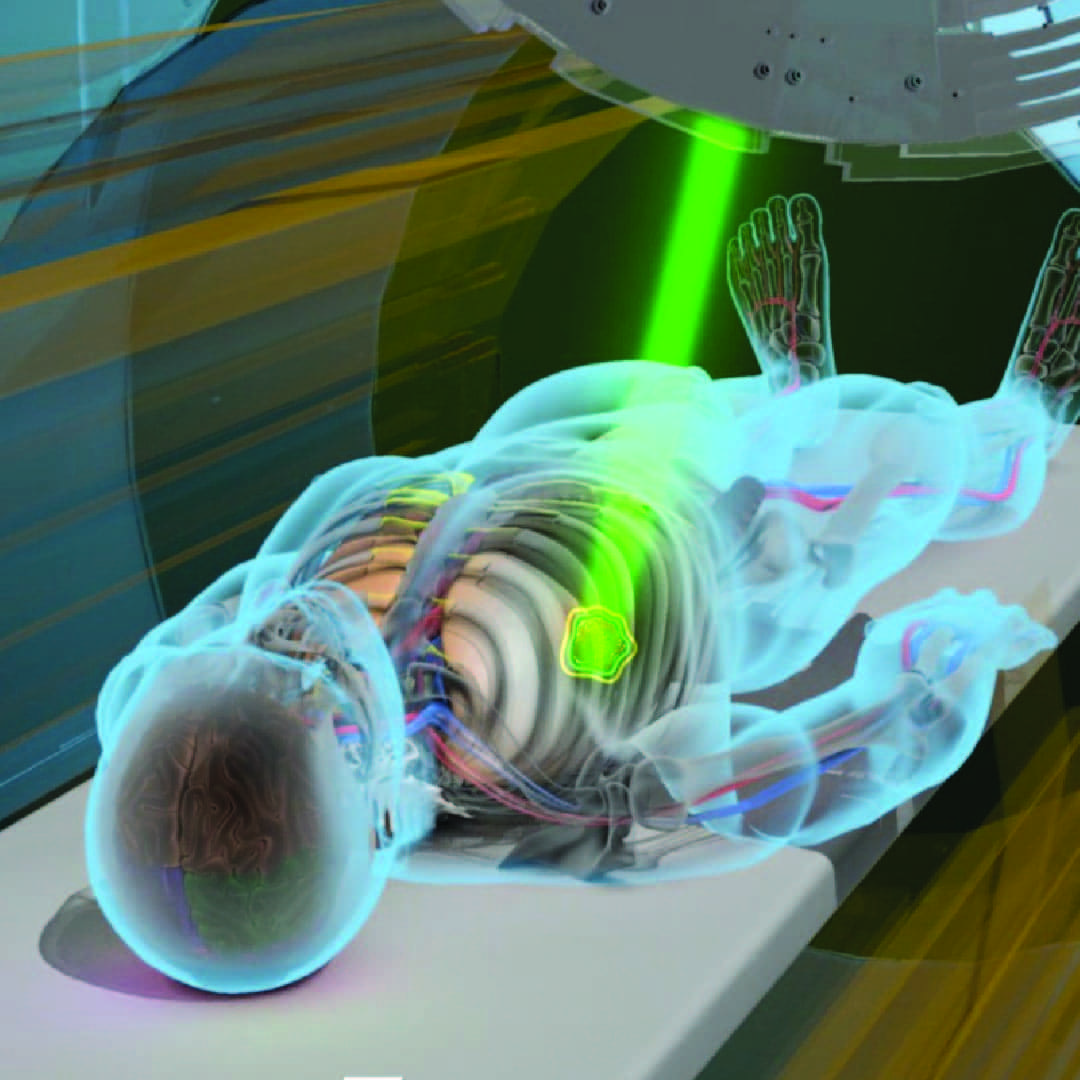
Personalized Treatment Planning
Simulation and CT-Based Planning
Every radiotherapy plan begins with a CT simulation, where the patient is positioned as they will be during actual treatment. This scan helps define the exact size, shape, and location of the tumor, allowing our team to plan the most accurate radiation delivery.
Multidisciplinary Team Review
Our radiation oncologists work closely with medical oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and pathologists to develop a coordinated treatment plan. This team-based approach ensures optimal timing and integration of radiotherapy within the overall cancer care pathway.
Custom Immobilization and Organ-Sparing Techniques
We use personalized immobilization devices (like thermoplastic masks or vacuum cushions) to keep the patient in the exact same position every day. Advanced techniques like image guidance, gating, and shielding are employed to protect nearby healthy tissues and organs.
Adaptive Planning in Selected Cases
In certain cancers where the tumor size or shape changes during treatment (e.g., head and neck or cervical cancers), we use adaptive radiotherapy. This involves re-planning midway to adjust for anatomical changes and ensure continuous precision.
Safety & Quality Assurance
Daily Machine QA and Weekly Physics Checks
Our medical physicists perform daily quality assurance (QA) checks on the TrueBeam STx machine to ensure it functions with consistent accuracy. Detailed weekly calibration and verification are also conducted to maintain the highest safety standards.
Real-Time Monitoring and Motion Management
We use advanced technologies like cone-beam CT, gated radiotherapy, and real-time tracking to monitor tumor position during treatment. This is especially crucial for tumors in moving organs like the lungs, liver, or breast.
Strict Radiation Safety Protocols for Patients and Staff
Radiation is delivered with utmost precision and under stringent safety protocols, adhering to international standards. Our treatment areas are shielded, staff use proper monitoring devices, and patients are educated about all safety measures before and during therapy.
Cancers Treated with Radiotherapy
- Head and Neck Cancers
- Brain and Spine Tumors
- Breast Cancer
- Lung and Esophageal Cancer
- Prostate and Genitourinary Cancers
- Gastrointestinal Malignancies
- Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors
- Pediatric Cancers
Personalized Treatment Planning
- Simulation and CT-based planning
- Multidisciplinary team review
- Custom immobilization and organ-sparing techniques
- Adaptive planning in selected cases
Safety & Quality Assurance
- Daily machine QA and weekly physics checks.
- Real-time monitoring and motion management.
- Strict radiation safety protocols for patients and staff.
Conclusion
At Andromeda Cancer Hospital, our commitment to excellence in radiation therapy is driven by our mission to provide the highest quality cancer care with compassion, precision, and innovation. With cutting-edge technology like the Varian TrueBeam STx, personalized treatment planning, and a multidisciplinary team approach, we deliver world-class radiotherapy tailored to each patient’s unique clinical needs.
Whether the goal is cure, control, or comfort, our expert team ensures that every patient receives the safest and most effective radiation treatment available. By continuously adopting global best practices and embracing technological advancements, Andromeda Cancer Hospital stands at the forefront of cancer care in northern India—bringing hope, healing, and better outcomes to every patient we serve.
